Top 5 Effective Ways to Calculate the Area of a Pyramid
Understanding the area of a pyramid is essential for students and architects alike. Pyramids, characterized by their triangular faces and polygonal bases, hold significant importance in both mathematical contexts and real-world applications. This article will explore the pyramid area tutorials that cover the formulas used to determine not only the area but also the volume of pyramids, their geometric properties, and practical applications. We’ll share methods that apply to different types of pyramids, including rectangular and triangular bases, providing you with a solid foundation to calculate areas efficiently.
The Basics of Pyramid Geometry
Before diving into calculations, it’s important to understand the fundamental aspects of pyramid geometry. A pyramid consists of a base, which can be square, rectangular, or triangular, and triangular faces that converge at a point known as the apex of the pyramid. The base area of the pyramid can be computed from the dimensions of its base shape, while the height of the pyramid, which is crucial for area calculations, is measured perpendicularly from the base to the apex.
Understanding Base Area Calculations
The first step in calculating the area of a pyramid is determining the base area. For instance, if the base is a square, the formula is straightforward: \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \). For rectangular bases, it becomes \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \). If dealing with a triangular base, the area can be found using \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height of the triangle} \). Mastering these calculations sets the foundation for obtaining the complete surface area calculation for the pyramid.
Calculating the Height of a Pyramid
The height of a pyramid is vital in computations, especially for finding the lateral surface area and overall surface area. To find the height, you can apply the Pythagorean theorem in cases where slant height is known. The slant height is the distance from the apex to the midpoint of a base edge. This can be expressed as \( \text{height} = \sqrt{(\text{slant height})^2 – (\frac{\text{base edge}}{2})^2} \). Understanding this aspect of pyramid geometry is crucial for accurate calculations of both volume and area.
Formulas for Pyramids
Once the base areas and the height of a pyramid are known, the related formulas make calculating the area both manageable and precise. The various pyramid geometry formulas help students and professionals alike in providing clear mathematical solutions to their pyramid-related calculations.
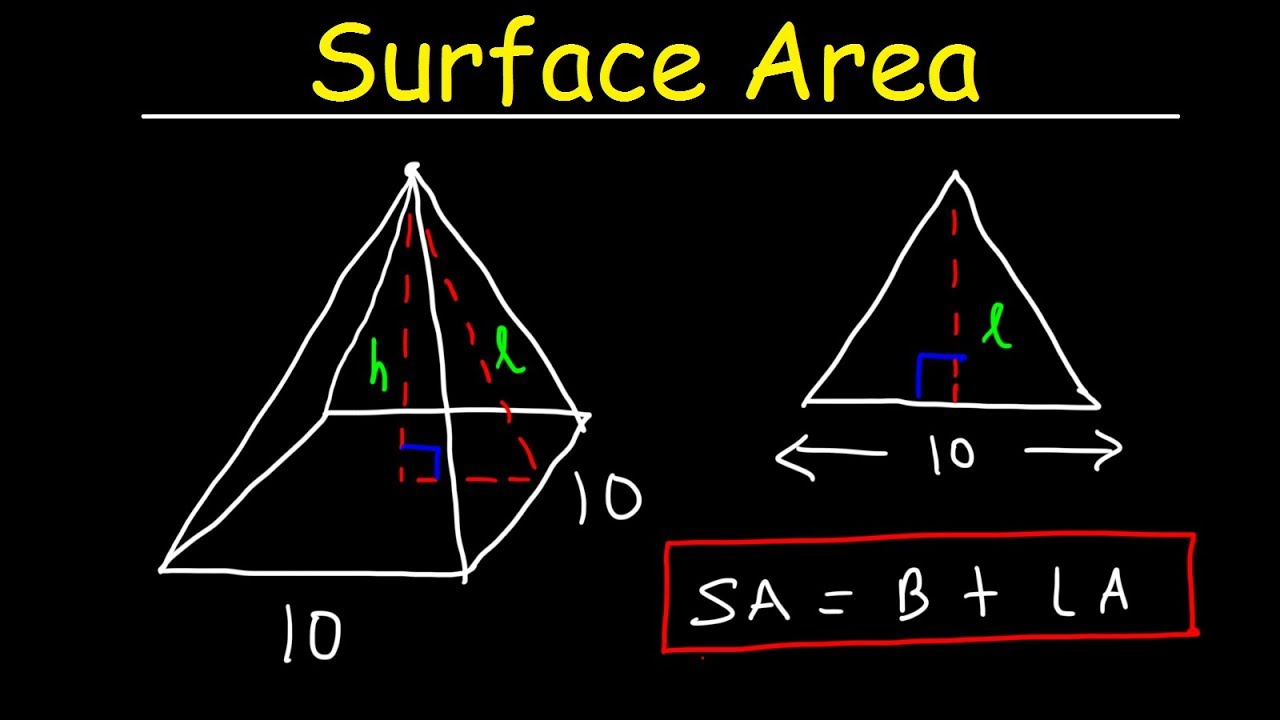
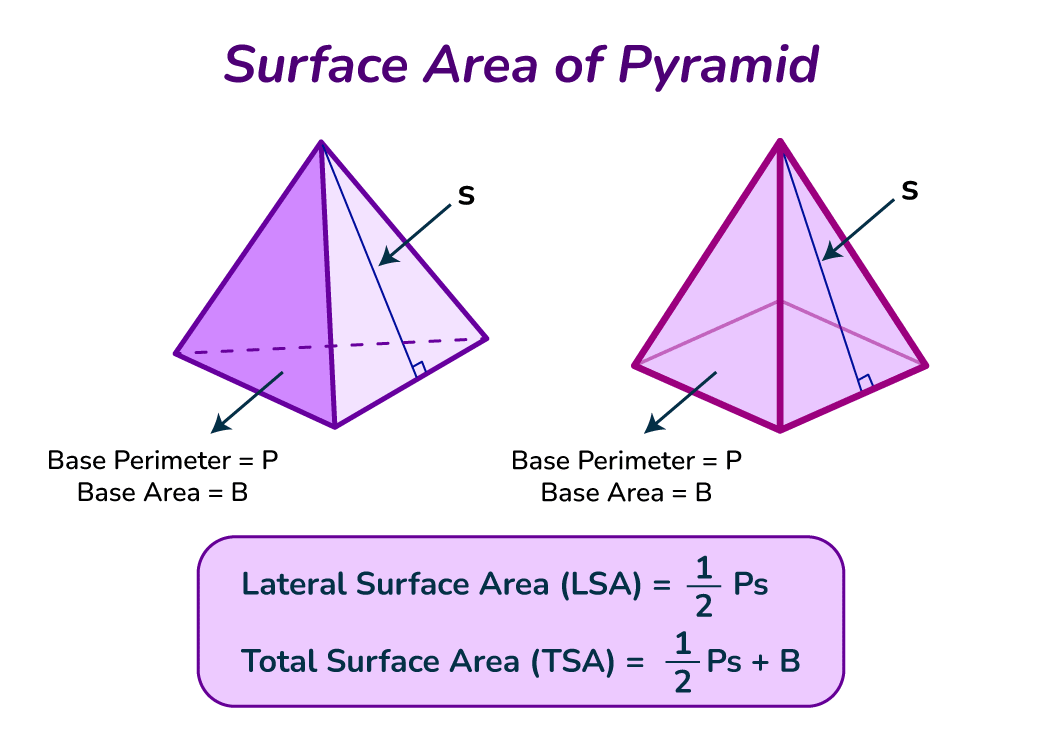
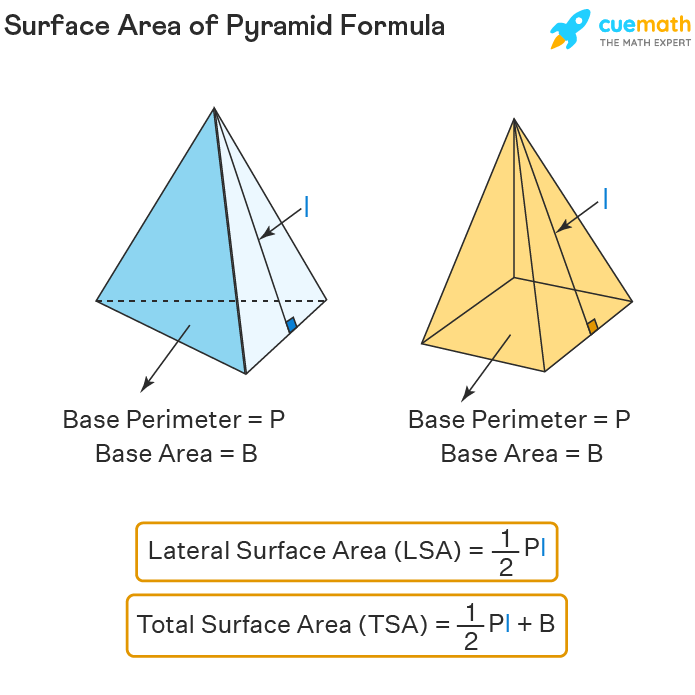
Using Pyramid Formula for Surface Area
To calculate the pyramid lateral surface area, one can use the formula: \( \text{Lateral Surface Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base perimeter} \times \text{slant height} \). Adding the base area to this lateral surface area gives you the total surface area: \( \text{Total Surface Area} = \text{Base Area} + \text{Lateral Surface Area} \). Visual aids such as diagrams can simplify the understanding of this concept, allowing one to visualize how the areas interact in a geometric sense.
Pyramid Volume Formula
The pyramid volume formula is also essential in studies relating pyramids. It is calculated as \( \text{Volume} = \frac{1}{3} \times \text{Base Area} \times \text{Height} \). This formula vividly illustrates how the volume relates to both the base dimensions of the pyramid and its height, encapsulating the three-dimensional properties of the geometric figure. This further emphasizes the connection among volume, area, and the properties of a pyramid.
Practical Examples and Applications
Applying these formulas in real-life contexts helps reinforce the theoretical understanding of pyramids. Whether in architecture or education, understanding how to find areas of pyramids proves beneficial.
Real-World Examples of Pyramids
Pyramids are universally recognized, with some historic structures standing as prime examples, such as the Pyramids of Giza. In architecture, recognizing their significance helps better appreciate the intersection of mathematics and artistry in design. Knowing how to calculate the area is essential when creating architectural models for pyramidal structures, employing the principles of geometry and architectural design standards.
Hands-On Activities with Pyramids
Hands-on experiences can greatly enhance our understanding of pyramids. Creating pyramid models from various materials can allow students to experience firsthand how to measure and calculate areas. By applying formulas in practical exercises, they can comprehend the relationship between height, base dimensions, and area effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the different types of pyramids and their properties is essential for accurate calculations.
- Learning methods to determine the height and area make calculations more efficient.
- Applying real-world contexts enriches the mathematical concepts involved with pyramids.
- Utilizing hands-on projects and tools fosters a deeper comprehension of pyramid geometry.
- Understanding the differentiation between volume and surface area enhances mathematical applications in geometry.
FAQ
1. What are the different methods to determine the volume and area of a pyramid?
There are several methods to determine both volume and area based on the type of pyramid. For example, square pyramids’ area is calculated using \( \text{Total Surface Area} = \text{base area} + \text{lateral surface area} \), while volume is computed as \( \text{Volume} = \frac{1}{3} \times \text{Base Area} \times \text{Height} \). The key is understanding the pyramid’s properties, whether it has a square or triangular base.
2. How can I visualize the calculations for pyramid areas?
Visualizing calculations can be facilitated through the use of diagrams that illustrate different pyramid shapes, base dimensions, and the relationships between height, base area, and slant height. Resources and online tools offer educational diagrams that can enhance conceptual understanding of how area is formulated across various pyramid designs.
3. Are there educational projects that focus on teaching pyramids?
Absolutely! Hands-on projects where students create pyramids from cardboard or other materials can effectively teach the properties of pyramids. Combining design with mathematical calculations allows a practical approach to understanding geometric concepts, enriching the overall learning experience.
4. What are the slant height and its significance in area calculations?
The slant height is the length from the apex of the pyramid to the midpoint of a base edge. It is significant in calculating the lateral surface area and understanding the overall structure of the pyramid. Accurate assessment of slant height directly impacts how surface area is calculated, influencing both area and volume determination.
5. How can I find additional resources on pyramid formulas?
There are numerous resources available online for further study of pyramid geometry formulas. Websites dedicated to mathematics often offer comprehensive tutorials, interactive geometry tools, and graphical aids to enhance understanding and clarity when working with pyramids and their properties.